Selection Sort
Selection sort is conceptually the simplest sorting algorithm. This algorithm will first find the smallest element in the array and swap it with the element in the first position, then it will find the second smallest element and swap it with the element in the second position, and it will keep on doing this until the entire array is sorted. It is called selection sort because it repeatedly selects the next-smallest element and swaps it into the right place.
This sorting algorithm is an in-place comparison-based algorithm in which the list is divided into two parts, the sorted part at the left end and the unsorted part at the right end. Initially, the sorted part is empty and the unsorted part is the entire list.
The smallest element is selected from the unsorted array and swapped with the leftmost element, and that element becomes a part of the sorted array. This process continues moving unsorted array boundary by one element to the right.
This algorithm is not suitable for large data sets as its average and worst case complexities are of Ο(n2), where n is the number of items.
How Selection Sort Works?
Following are the steps involved in selection sort (for sorting a given array in ascending order):
- Starting from the first element, we search the smallest element in the array, and replace it with the element in the first position.
- We then move on to the second position, and look for smallest element present in the subarray, starting from index 1, till the last index.
- We replace the element at the second position in the original array, or we can say at the first position in the subarray, with the second smallest element.
- This is repeated, until the array is completely sorted.
Let's consider an array with values {3, 6, 1, 8, 4, 5}
Below, we have a pictorial representation of how selection sort will sort the given array.
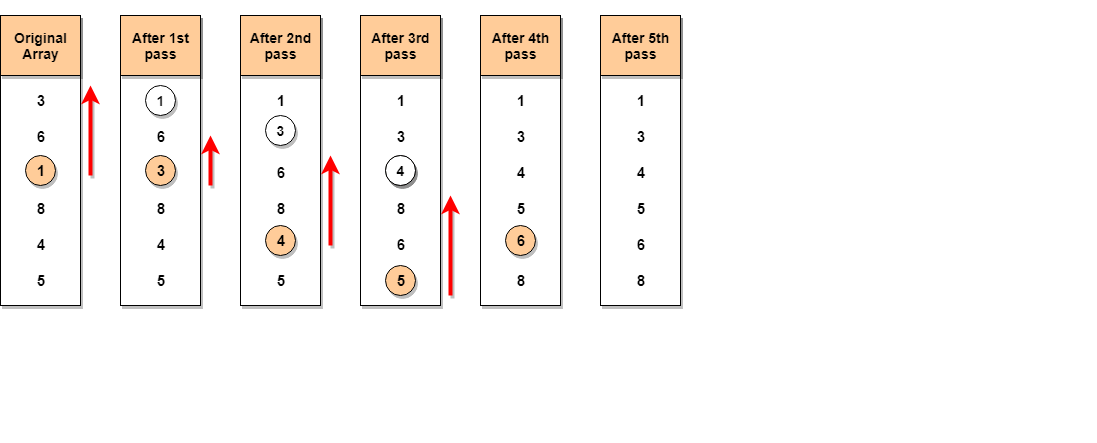
In the first pass, the smallest element will be 1, so it will be placed at the first position.
Then leaving the first element, next smallest element will be searched, from the remaining elements. We will get 3 as the smallest, so it will be then placed at the second position.
Then leaving 1 and 3 (because they are at the correct position), we will search for the next smallest element from the rest of the elements and put it at third position and keep doing this until array is sorted.
Code
// C program implementing Selection Sort
# include <stdio.h>
// function to swap elements at the given index values
void swap(int arr[], int firstIndex, int secondIndex)
{
int temp;
temp = arr[firstIndex];
arr[firstIndex] = arr[secondIndex];
arr[secondIndex] = temp;
}
// function to look for smallest element in the given subarray
int indexOfMinimum(int arr[], int startIndex, int n)
{
int i;
int minValue = arr[startIndex];
int minIndex = startIndex;
for(i = minIndex + 1; i < n; i++) {
if(arr[i] < minValue)
{
minIndex = i;
minValue = arr[i];
}
}
return minIndex;
}
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int index = indexOfMinimum(arr, i, n);
swap(arr, i, index);
}
}
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {46, 52, 21, 22, 11};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Unsorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
selectionSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output
Unsorted array:
46 52 21 22 11
Sorted array:
11 21 22 46 52
Selection Sort Algorithm
- Set MIN to location 0
- Search the minimum element in the list
- Swap with value at location MIN
- Increment MIN to point to next element
- Repeat until list is sorted
Selection Sort Pseudocode
procedure selection sort
list : array of items
n : size of list
for i = 1 to n - 1
/* set current element as minimum*/
min = i
/* check the element to be minimum */
for j = i+1 to n
if list[j] < list[min] then
min = j;
end if
end for
/* swap the minimum element with the current element*/
if indexMin != i then
swap list[min] and list[i]
end if
end for
end procedure
Data Structures
Data Structures Overview Arrays Linked List Stack Queue Priority QueueExpression parsing
Infix Notation Prefix Notation Postfix notation Notation ConversionHashing
Hash Table and Function Collision ResolutionSearching Techniques
Linear Search Binary Search Interpolation Search Fibonacci SearchSorting
Bubble Sort Bubble Sort in Depth Selection Sort Selection Sort in Depth Insertion Sort Insertion Sort in Depth Shell Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Quick Sort in Depth Counting Sort Radix Sort Bucket SortTree
Trees and Graphs Binary Tree Types of Binary Trees Binary Search Tree N-ary Tree AVL Tree Red Black Tree Splay tree B tree B+ treeTree Search Traversal Techniques
Breadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) Inorder, Preorder and Postorder TraversalHeaps
Heaps Introduction Binary Heap Heap OperationsTrending
C Programming
Remember to follow community guidelines and don't go off topic.