Quick Sort
Quick sort is an algorithm of Divide and Conquer type.
Divide: Rearrange the elements and split arrays into two sub-arrays and an element in between search that each element in left sub array is less than or equal to the average element and each element in the right sub- array is larger than the middle element.
Conquer: Recursively, sort two sub arrays.
Combine: Combine the already sorted array.
Quick Sort is also based on the concept of Divide and Conquer, just like merge sort. But in quick sort all the heavy lifting (major work) is done while dividing the array into sub arrays, while in case of merge sort, all the real work happens during merging the sub-arrays. In case of quick sort, the combine step does absolutely nothing.
It is also called partition-exchange sort. This algorithm divides the list into three main parts:
- Elements less than the Pivot element
- Pivot element(Central element)
- Elements greater than the pivot element
Pivot element can be any element from the array; it can be the first element, the last element or any random element.
Quick sort by taking first element as Pivot
Step 1.
| 10 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 5 | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i low |
j high |
Pivot = arr[low];
i=low; j=high;
increment i until arr[i] > Pivot;
decrement j until arr[j] <= Pivot;
swap (arr[i],arr[j]);
if j < i
(swap Pivot,a[j]);
| 10 | 16 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 5 | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | j |
swap (a[i],a[j]);
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|
Step 2.
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | j |
swap (a[i],a[j]);
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 12 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|
Step 3.
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 15 | 6 | 3 | 12 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| i | j |
swap (a[i],a[j]);
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 15 | 12 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|
Step 4.
| 10 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 15 | 12 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| j | i |
j < i
swap (Pivot,a[j]);
| 6 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 3 | 10 | 15 | 12 | 16 | ∞ |
|---|
10 has been placed in its proper position.
Now the list has been divided into two sub list [6,5,8,9,3] and [15,12,16] with 10 in its proper position. Again partition the sub lists with assuming 6 and 15 as pivot element. Repeat partitioning and applying quick sort on the sub lists until the entire list gets sorted.
Quick Sort Algorithm
Quick-Sort(l,h)
{
If (l<h)
{
j=partition(l,h);
Quick-Sort(l,j);
Quick-Sort(j+1,h);
}
Partition(l,h)
{
pivot=a[l];
i=l;j=h;
while(i<j)
{
do
{
i++;
} while (a[i]<pivot);
do
{
j--;
} while (a[j]>=pivot);
If (i < j)
Swap(a[i],a[j]);
}
Swap(pivot,a[j]);
Return j;
}
Quick sort by taking last element as Pivot
The following diagram shows the working of quick sort algorithm where the last element is taken as pivot.
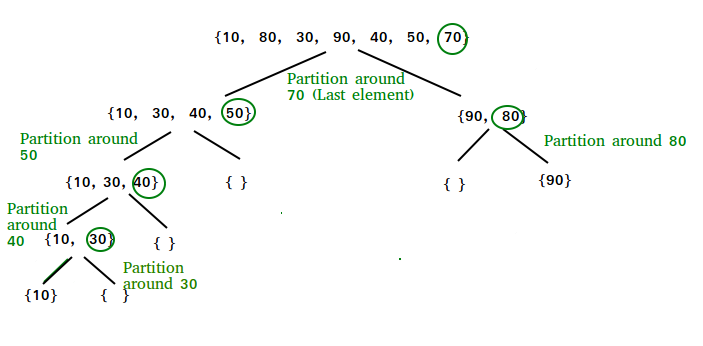
Pseudocode for Quicksort with last element as Pivot
/* low --> Starting index, high --> Ending index */
quickSort(arr[], low, high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now
at right place */
pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1); // Before pi
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high); // After pi
}
}
Pseudocode for Partition
/* This function takes last element as pivot, places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, and places all smaller (smaller than pivot)
to left of pivot and all greater elements to right
of pivot */
partition (arr[], low, high)
{
// pivot (Element to be placed at right position)
pivot = arr[high];
i = (low - 1) // Index of smaller element
for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap arr[i] and arr[j]
}
}
swap arr[i + 1] and arr[high])
return (i + 1)
}
C implementation of QuickSort
Code
#include<stdio.h>
// A utility function to swap two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
/* This function takes last element as pivot and places
the pivot element at its correct position in sorted
array, then it places all smaller items (smaller than pivot)
to left of the pivot and all greater elements to right of the pivot */
int partition (int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high]; // pivot
int i = (low - 1); // Index of smaller element
int j;
for (j = low; j <= high- 1; j++)
{
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if (arr[j] < pivot)
{
i++; // increment index of smaller element
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
/* The main function that implements QuickSort
arr[] --> Array to be sorted,
low --> Starting index,
high --> Ending index */
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
if (low < high)
{
/* pi is partitioning index, arr[p] is now
at right place */
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// Separately sort elements before
// partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
/* Function to print an array */
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i=0; i < size; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int arr[] = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Unsorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
quickSort(arr, 0, n-1);
printf("Sorted array: \n");
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
Output
Unsorted array:
10 7 8 9 1 5
Sorted array:
1 5 7 8 9 10
Data Structures
Data Structures Overview Arrays Linked List Stack Queue Priority QueueExpression parsing
Infix Notation Prefix Notation Postfix notation Notation ConversionHashing
Hash Table and Function Collision ResolutionSearching Techniques
Linear Search Binary Search Interpolation Search Fibonacci SearchSorting
Bubble Sort Bubble Sort in Depth Selection Sort Selection Sort in Depth Insertion Sort Insertion Sort in Depth Shell Sort Merge Sort Quick Sort Quick Sort in Depth Counting Sort Radix Sort Bucket SortTree
Trees and Graphs Binary Tree Types of Binary Trees Binary Search Tree N-ary Tree AVL Tree Red Black Tree Splay tree B tree B+ treeTree Search Traversal Techniques
Breadth First Search (BFS) Depth First Search (DFS) Inorder, Preorder and Postorder TraversalHeaps
Heaps Introduction Binary Heap Heap OperationsTrending
C Programming
Remember to follow community guidelines and don't go off topic.